Trace: • GP-Simulator Operation Manual
Table of Contents
GP-Simulator Operation Manual
GUI Description
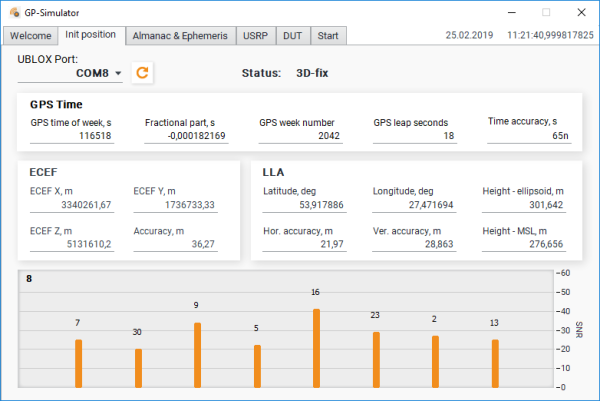
Init Position Tab
In the “Init position” tab, you can configure the connection to the UBLOX receiver for getting the current coordinates, accuracy, as well as time, and information about the satellites being observed.
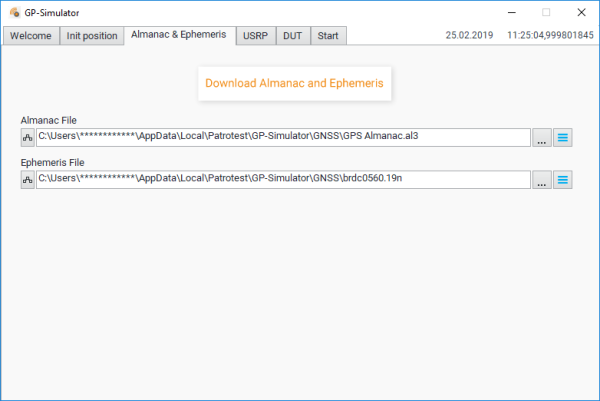
Almanac and Ephemeris Folder
Once the current time is determined, you can download the Ephemeris and Almanac files.
You need internet connection to download the corresponding files.
You can preload the Ephemeris and Almanac files on your computer and then define the path to the files in the corresponding fields.
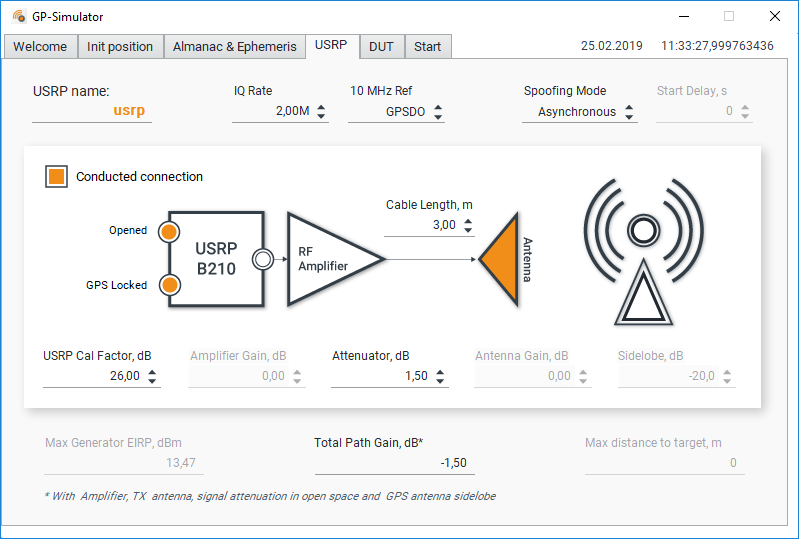
USRP Tab
The “USRP” tab provides the following settings/adjustments:
- USRP name - the name of your USPR board that you preset in NI-USRP Configuration Utility;
- IQ Rate - IQ sample rate. The minimal value is “1.5 MH.” The maximal value is “5 MHz.” The higher the value you input, the more CPU on your computer devices is used/loaded;
- 10 MHz Ref - The source of “10 MHz” reference frequency: External or GPSDO. In the cases when you work with antennas, GPSDO on your USRP board will be spoofed, so you need to use external high quality reference source;
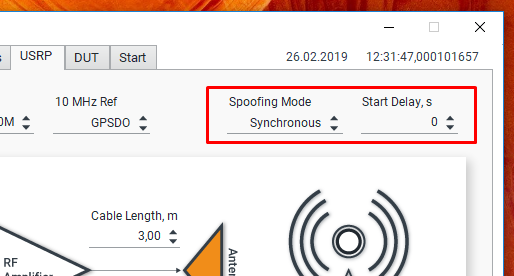
- Spoofing mode - Asynchronous or Synchronous. To learn more, read our article about different types of spoofing;
- Start delay, s - Generation start offset for synchronous mode. Can be used to study the required accuracy of signal synchronization;
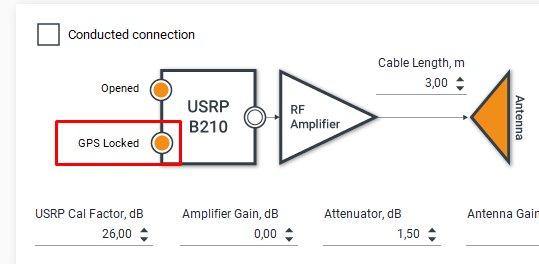
- Conducted connection flag - Should be set in case you use cable connection to the DUT. In case you work with an antenna, do not uncheck the corresponding box;
- Opened flag - Displayed in case of successful USRP initialization;
- GPS locked flag - Displayed in case of successful USRP GPSDO 3D-fix. If the corresponding flag is set, only synchronous generation is available;
- Cable Length, m - The total length of all applied cables. Used for calculating the Total Path Gain;
- USRP Cal Factor, dB - USRP calibration value. The calibration procedure described in - USRP Calibration Procedure;
- Amplifier Gain, dB - In the cases of radiated testing, set the gain of the external RF power amplifier;
- Attenuator, dB - The total path of attenuation in the cables and\or attenuators;
- Antenna Gain, dB - In the cases of radiated testing, set the corresponding antenna gain;
- Sidelobe, dB - Sidelobe of the DUT's receiving antenna that takes into account signal's angle of arrival. Used for calculating simulator's signal power in the phase center of the DUT antenna;
- Max Generator EIRP, dBm - Maximum availability of the generator's Effective Isotropic Radiated Power with a particular amplifier, antenna, and cables;
- Total Path Gain, dB - Calculated taking into account the antenna gain, power amplifier, as well as attenuation in cables and sidelobe of the receiver antenna;
- Max distance to target - Maximum available distance to the DUT.
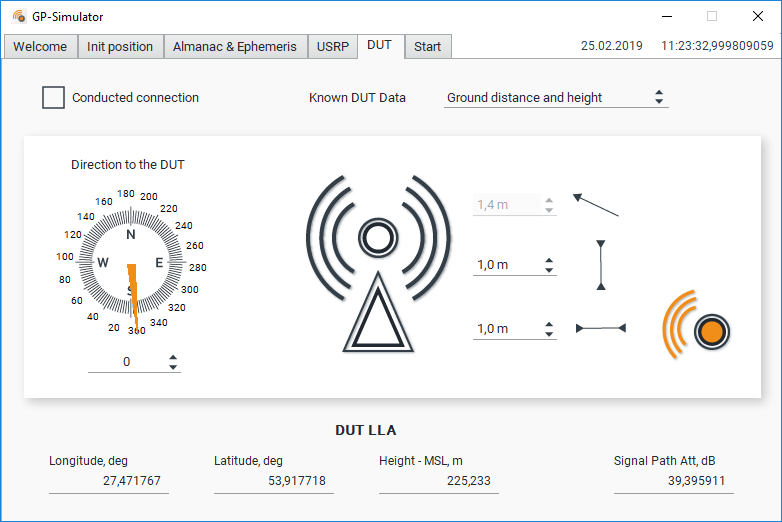
DUT Tab
In the “DUT” tab, you can set the distance and direction to the sample when carrying out field testing:
The user can determine the distance to the sample using the following two methods:
- Calculating the distance to the DUT on the ground and the height of the DUT;
- Calculating the distance required for getting on the ground and in the line of sight.
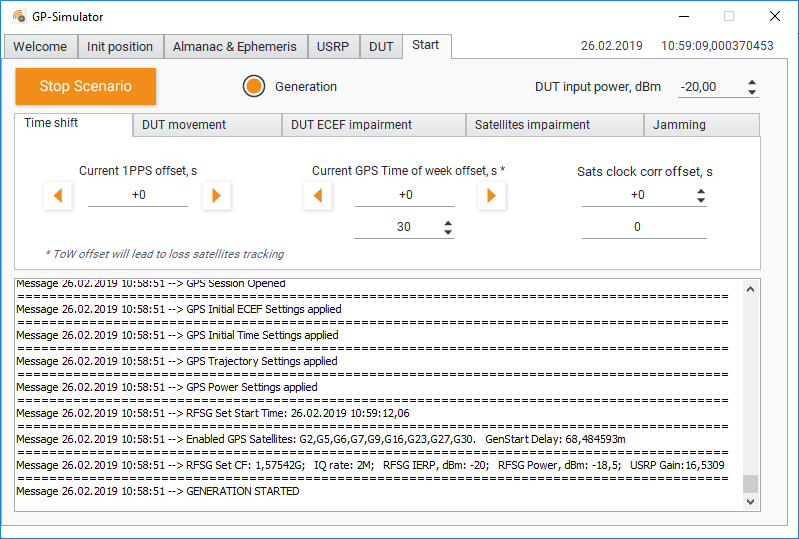
Start Tab
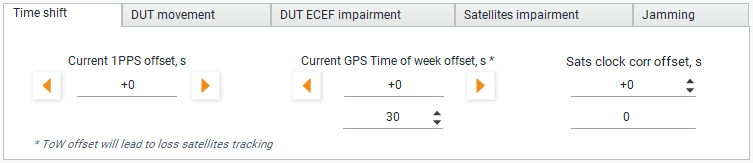
Time Shift Tab
In the “Time shift” tab, you can shift the 1PPS or timestamp of the DUT in different ways.
- Current 1PPS offset, s - Adds an offset to the generated sequence in the way that it shifts the 1PPS signal of the DUT;
- Current GPS Time of week offset, s - Dramatically changes the ToW in HOW in all subframes. The position of all satellites is recalculated based on the new time. Thus, the receiver temporarily stops tracking the satellites. Make sure that the power level of the generated signal is sufficient enough to block the real signals;
- Sats clock corr offset, s - Synchronously simulates clock drift on all satellites. Leads to a smooth drift of the DUT 1PPS impulse.
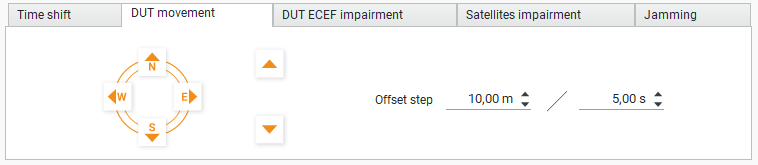
DUT Movement Tab
In the “DUT movement” tab, you can move the coordinates of the DUT for a certain number of meters for a certain time period.
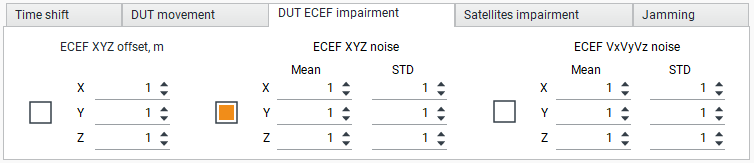
DUT ECEF Impairment Tab
This tab is experimental. In the “DUT ECEF impairment” tab, can you add a fixed offset and noise to the coordinates of the DUT and noise to the Doppler offset. You can also set the “Mean” value and the standard deviation (STD) of the noise.
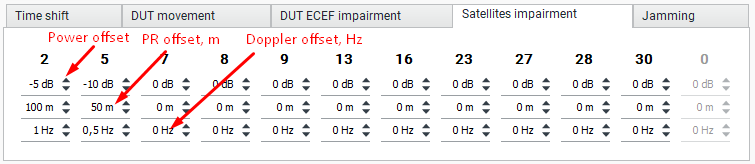
Satellites Impairment Tab
In the “Satellites impairment” tab, you can set the relative power, pseudorange offset and Doppler offset for each satellite.
Conducted testing
Below is displayed the diagram of typical DUT testing for vulnerabilities to spoofing and jamming.
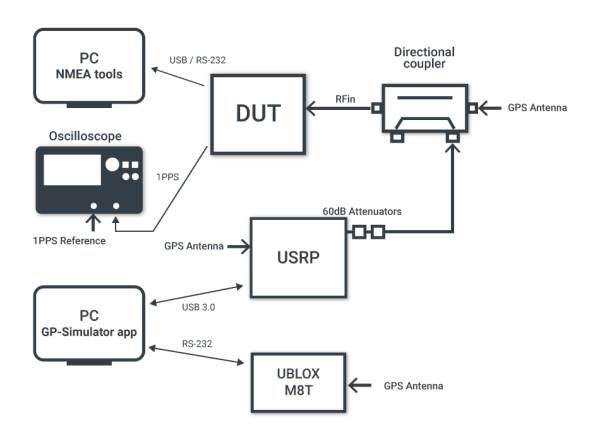
We recommend using a directional coupler for injecting the simulated signal into the real one. Oscilloscope is used for measuring 1PPS impulse offset.
Application Settings
First, wait for the “UBLOX M8T” status to display “3D Fix.” Then, sownload almanac and ephemeris files.
After that, set the following in the “USRP” tab:
- 10 MHz Ref to GPSDO;
- Check the “Conducted Connection” box;
- Set the “Attenuator” value based on cables, attenuators and the directional coupler.
In the “Start: folder setup
- DUT input power. Usually it is within the ”-100 dBm“ range;
- Click on the “Start” button.
Radiated Testing
NOTE: The use of radiated radio signals may be illegal in your country. Please familiarize yourself with your local legal laws on the regulation of the radio spectrum before using this app. We are not responsible for your actions.
Below is displayed the diagram of a typical use case of our equipment for field testing vulnerability of various devices to GPS spoofing exposure.
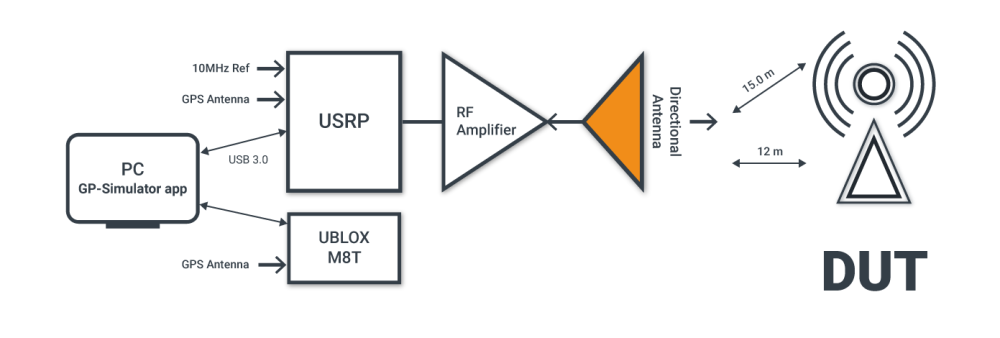
In the case of radiated testing, you cannot use internal USRP GPSDO as a “10 MHz” reference source, because it will be spoofed. Thus, you should use external high quality reference source. The frequency stability should be better than “25 ppb.”
Application Settings
First, wait for the “UBLOX M8T” status to display “3D Fix.” After that, download almanac and ephemeris files.
In the “USRP” tab, set the following:
- 10 MHz Ref to External;
- Uncheck the “Conducted Connection” box;
- Set “Amplifier Gain,” “Attenuator,” and “Antenna Gain” according to your connected equipment.
In the “DUT” tab, set the following:
- Direction to DUT;
- and known distances.
In the “Start” tab, set up the following:
- DUT input power that is usually it is within the ”-100 dBm“ range;
- Click on the “Start” button.
Synchronous and asynchronous mode
In the case of an asynchronous attack, a spoofer transmits false signals that are stronger than the original ones, causing the receiver to lose track of the satellites and lock on to the overpowering spoofing signal(s). On the other hand, synchronous attacks imply transmitting signals that are synchronized with the original ones and then gradually overpowering the latter.
You can learn more about the difference between synchronous and asynchronous attacks in our dedicated article on this page.
In the “Synchronous” mode, our simulator generates a signal that is aligned with the real one up to “100 ns.” To select a particular spoofing mode, go to the “USRP” tab.
If you select the “Synchronous” mode, then you can set an additional offset for the start of the generation. This is convenient for examining the DUT correlation analysis window.
To work in the “Synchronous” mode, you need to wait for the following flag: “GPS Locked”:
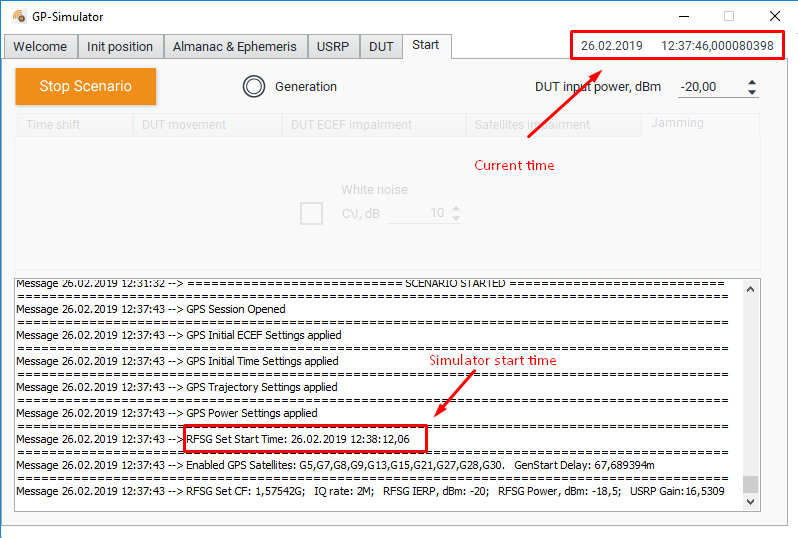
In the “Synchronous” mode, the generation does not start immediately, but only at a particular time: